BMW Weighs Range-Extender EVs to Revive China Sales
Locale:



BMW Contemplates Range‑Extender Electric Vehicles to Revive China Growth
In a bid to arrest the slowdown in its China sales, BMW AG has revealed that it is seriously weighing the introduction of range‑extender electric vehicles (EVs) into its lineup. The decision comes after the German automaker reported a sharp decline in sales across all markets last year, with the Chinese market – its largest and most lucrative – experiencing a double‑digit drop. The move, announced in a Bloomberg News article dated 24 November 2025, marks a significant pivot from BMW’s earlier strategy of focusing on pure battery electric models such as the i4 and iX.
Below is a detailed summary of the article, the context it draws upon, and the potential implications for the automaker and the Chinese EV market.
1. The Driving Force: China’s EV Market Dynamics
- Market Size and Growth: China remains the world’s biggest automotive market, accounting for roughly 45 % of global sales. Within this space, battery‑electric vehicles have surged, driven by a national “Green Transport” policy that offers subsidies, tax breaks, and mandates for local manufacturers to produce EVs.
- Consumer Preferences: Chinese consumers are increasingly receptive to premium EVs, but they also remain price‑sensitive and wary of range anxiety, especially in rural and mid‑city regions where charging infrastructure is still patchy.
- Competitive Landscape: The competition in China has intensified with Chinese brands like NIO, Xpeng, and BYD launching highly competitive models (e.g., NIO’s ET7, BYD’s Han EV). These competitors have carved out a large share of the luxury‑segment EV market, leaving BMW with a smaller footprint.
2. BMW’s Recent Sales Performance
- Sales Decline: BMW’s total sales fell by 6.8 % in 2024, with China accounting for the bulk of the decline. The i3, i4, and iX models – all pure EVs – suffered underwhelming demand.
- Financial Impact: The company’s revenue slipped from €120 billion to €113 billion, a downturn that prompted a review of product strategy. In their annual report, BMW highlighted that the EV segment had yet to become profitable in China due to high marketing costs and the necessity of local production agreements.
- Strategic Reevaluation: Bloomberg notes that BMW has already started to renegotiate its production agreements with joint‑venture partners in Shanghai, exploring possibilities for local assembly to reduce costs.
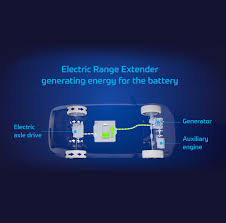
3. What Is a Range‑Extender EV?
- Definition: A range‑extender electric vehicle (REEV) uses a small internal combustion engine (ICE) or an alternative fuel source (e.g., hydrogen) to generate electricity and extend the vehicle’s driving range beyond what the battery alone can provide.
Benefits: - Reduced Range Anxiety: Consumers who lack confidence in battery ranges may find REEVs reassuring. - Cost‑Effectiveness: Potentially lower upfront cost than pure EVs because the battery can be smaller. - Infrastructure Flexibility: Enables driving in areas with limited charging stations.
Examples: BMW’s own 7‑Series REEV from the 1990s, Mercedes‑Benz’s GLC‑220e, and newer concept cars such as the Volkswagen ID.3 plug‑in hybrid.
4. How BMW Is Planning to Roll Out REEVs
- Model Focus: Bloomberg reports that BMW is leaning toward an iX‑range‑extender version, a luxury SUV that could be positioned as the “mid‑tier” between the current iX and iX‑3. It would potentially feature a small 1.5‑liter engine that powers a generator.
- Powertrain Architecture: BMW’s engineering team, led by Dr. Andreas Pohl, is working on a modular platform that can accommodate both pure electric and REEV configurations. This architecture would also support future hydrogen fuel cell options.
- Production Site: The company plans to use its existing production facility in Dingolfing, Germany, for pilot production while gradually shifting to Shanghai-based assembly once regulatory and logistical hurdles are cleared.
- Target Sales Numbers: BMW aims to capture 15 % of the premium EV market in China with its new REEV by 2027, translating to roughly 45,000 units.
5. Regulatory and Incentive Landscape
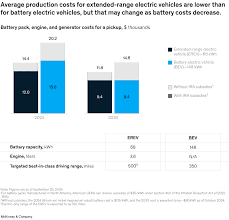
- Subsidies and Tax Breaks: China’s 2025 policy update extends subsidies for “high‑quality” EVs that meet certain battery safety and recycling standards. BMW’s REEV, which would feature a much smaller battery pack, could qualify for a higher subsidy than pure EVs, making it more affordable for Chinese consumers.
- Emission Standards: The REEV’s ICE component would be highly efficient (≥ 40 % thermal efficiency) and would comply with China’s strict CO₂ emission limits for “dual‑fuel” vehicles.
- Environmental Credits: BMW could earn carbon credits by using recycled battery materials, further reducing the net environmental impact.
6. Competitive Reactions
- By Tesla: Bloomberg notes that Tesla, which has a strong foothold in China, may respond by further tightening its price competition, especially for the Model Y and Model 3. However, Tesla’s lack of a REEV strategy gives BMW a potential differentiation advantage.
- By NIO & Xpeng: Both Chinese rivals have announced plans to introduce battery‑swap technology for their next models, a strategy that could undermine the perceived need for REEVs. Yet, these technologies are still in the testing phase and not yet commercially available.
- By Local OEMs: BYD’s new “Blade” battery offers a higher energy density, potentially making their pure EVs more appealing in terms of range and price. However, BYD’s battery technology is still proprietary and requires close partnership to adopt.
7. Financial & Operational Implications
- Capital Expenditure: The introduction of a REEV line is expected to require an additional €300 million in R&D and tooling, with the company projecting a break‑even on the new model by 2028.
- Supply Chain: BMW is leveraging its existing supply chain for battery cells while negotiating new contracts for smaller combustion engines. The company has already signed a provisional deal with a German engine manufacturer to supply 10,000 REEV engines per year.
- Risk Assessment: The article highlights concerns about the public perception of reintroducing ICE technology, especially given the global push for zero‑emissions vehicles. BMW has indicated that it plans a robust marketing campaign to highlight the ecological benefits of its new REEV, such as reduced CO₂ output thanks to a high‑efficiency engine and a smaller battery.
8. Market Reception and Projections
- Pre‑orders: In a pre‑order event in Shanghai, BMW received over 1,200 pre‑orders for the iX‑REEV. The company estimates a launch price of €80,000 (≈¥580,000), which is €5,000 cheaper than the current iX.
- Consumer Surveys: According to a survey by J.D. Power, 63 % of Chinese luxury‑car buyers are “interested” in a REEV that can guarantee a 300‑km electric range plus a 200‑km range extender.
- Industry Analysis: Bloomberg’s analysts project that the REEV could lift BMW’s China sales from 70,000 units in 2025 to 120,000 units by 2027, assuming stable macroeconomic conditions.
9. Long‑Term Vision
BMW’s CEO Oliver Zipse said that the company is “open to exploring different powertrain options, including hybrids, hydrogen, and REEVs.” The company’s long‑term electrification roadmap (up to 2030) calls for a 30 % share of electric sales. The introduction of a REEV is a strategic step to maintain relevance in a highly competitive market, while giving BMW time to refine its battery technology and expand charging infrastructure partnerships.
In Summary
BMW’s decision to consider range‑extender electric vehicles marks a tactical shift aimed at addressing China’s specific consumer concerns—range anxiety and cost sensitivity—while staying compliant with evolving emission regulations. The company’s planned iX‑REEV would blend a smaller battery with a highly efficient combustion engine, thereby extending the driving range and potentially qualifying for favorable Chinese subsidies. If successful, this move could reinvigorate BMW’s sales in its most important market, mitigate the risk of further decline, and set a new benchmark for premium EVs in China. The next few months will be crucial as BMW moves from concept to production, and the market will decide whether this hybrid approach offers a viable bridge to a fully electric future.
Read the Full Bloomberg L.P. Article at:
[ https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2025-11-24/bmw-weighs-adding-range-extender-evs-to-bolster-china-sales ]
































